📚 목차
[React] Context API로 전역 상태 관리하기
React Context API는 프로젝트의 상위/하위 컴포넌트 간 데이터 공유 방식이다.
Context API를 사용하면 state를 props로 전달하는 대신, 전역 상태를 관리할 수 있다.
React에서는 SSOT(Single Source of Truth) 원칙을 따르기 때문에, 컴포넌트의 상태는 항상 상위 컴포넌트에서 관리해야 한다.
그래서 보통 하나의 부모 컴포넌트에서 생성한 state를 여러 자식 컴포넌트에 state를 공유하려고 할 때, props를 통해서 전달했을 것이다.
하지만 이런 방식은 컴포넌트의 depth가 깊어질수록 props를 계속 전달해야 하기 때문에 props drilling`이라고 불리는 문제를 발생시킨다.
이를 해결하기 위해 Context API를 사용하면, 컴포넌트 트리의 깊은 곳에 있는 컴포넌트도 상위 컴포넌트에서 생성한 state를 쉽게 사용할 수 있다.
Context API란?
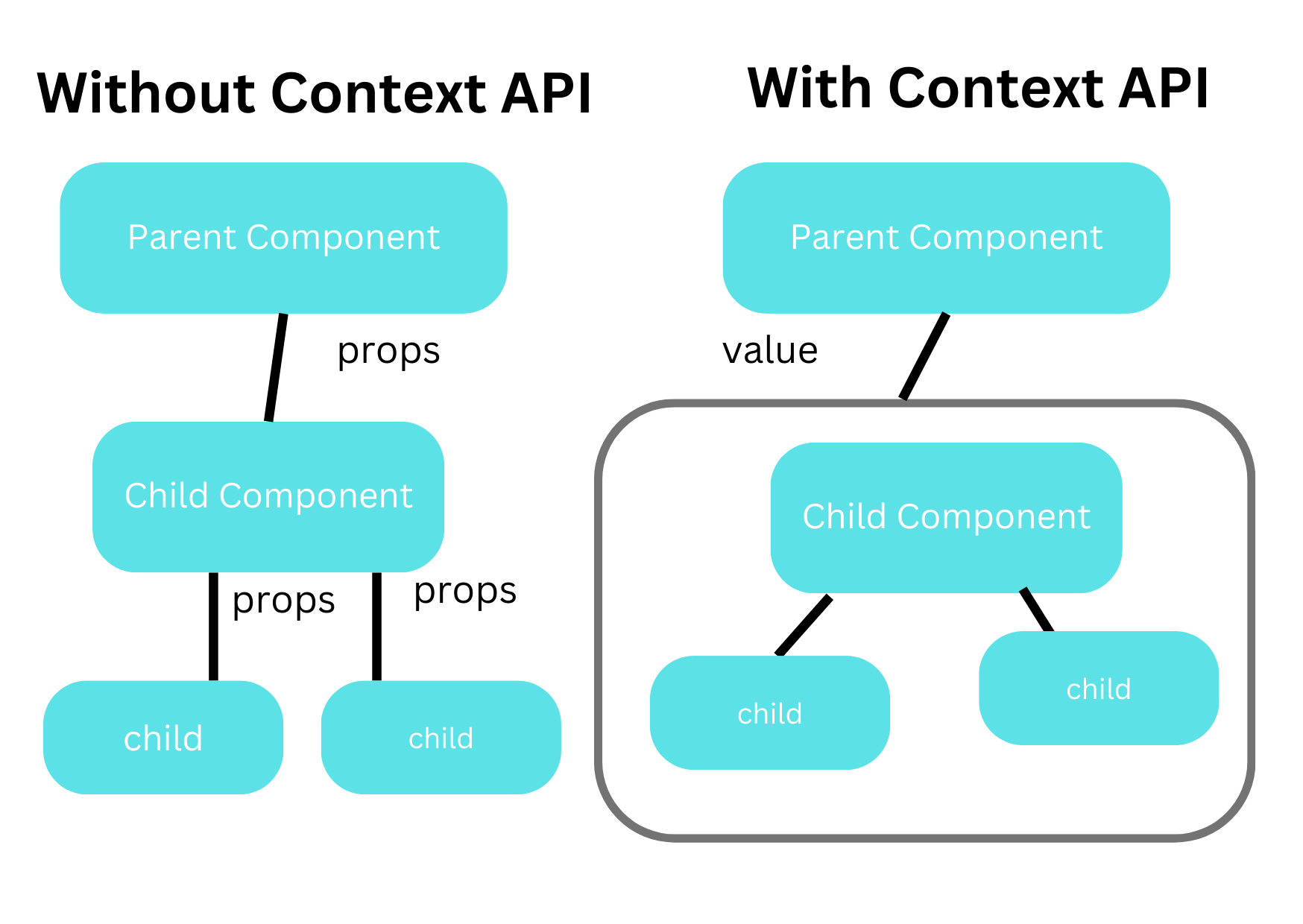
React의 Context API는 컴포넌트 트리 전체에 데이터를 전역으로 공유할 수 있는 방법이다.
일반적으로 여러 컴포넌트에 전달되어야 하는 데이터(state)를 prop drilling 없이 전역적으로 관리할 수 있다.
Context API 구성요소
createContext()
- 새로운
Context객체를 생성한다. - 이 객체에는 React 컴포넌트 트리에서 사용할 수 있는
Provider,Consumer가 포함되어 있다.
const UserContext = createContext(null);createContext(defaultValue)에서 defaultValue는 Provider가 없는 경우 사용할 기본값이다.
단, 실제 사용 시엔 항상 <Provider>로 값을 전달하는 것이 안전하다.
<Provider>
- Context를 사용하는 하위 컴포넌트들에게 값을 전달한다.
- 이 값은 value prop을 통해 설정한다.
<UserContext.Provider value={user}>
<App />
</UserContext.Provider>Context를 사용하는 모든 컴포넌트는 가장 가까운 Provider의 value를 참조한다.
동적으로 바뀌는 값도 전달 가능하다. 예: 로그인 상태, 테마, 언어 등.
주의사항
- value가 변경되면 해당 값을 구독 중인 모든 하위 컴포넌트가 리렌더링된다.
- 따라서 value는 useMemo()로 메모이제이션 하는 것이 좋다.
useContext()
- Context 값을 읽기 위해 사용하는 React Hook이다.
- 해당 Hook이 호출된 컴포넌트는 Provider로부터 value를 구독하게 된다.
const user = useContext(UserContext);클래스형 컴포넌트에서는 Context.Consumer를 사용했지만, 함수형 컴포넌트에서는 useContext()를 사용하는 것이 표준이다.
이 Hook은 컴포넌트 리렌더 시 자동으로 최신 값을 가져온다.
Context API 사용 예시
로그인한 사용자의 정보를 앱 전역에서 관리하는 시나리오를 Context API를 사용해 구현해보자
- src/contexts/UserContext.tsx
import { createContext, useState, useContext } from 'react';
// 사용자 정보 타입 정의
interface User {
id: number;
name: string;
email: string;
}
// Context 값의 타입 (user 상태 + 로그인/로그아웃 함수)
interface UserContextType {
user: User | null;
login: (userData: User) => void;
logout: () => void;
}
// 🟢 Context 생성
const UserContext = createContext<UserContextType | undefined>(undefined);
// 🟢 Provider 컴포넌트 (Provider로 데이터 공급 - 하위 컴포넌트에서 사용할 user 정보와 login/logout 함수를 전달)
export const UserProvider = ({ children }: { children: React.ReactNode }) => {
const [user, setUser] = useState<User | null>(null);
const login = (userData: User) => setUser(userData);
const logout = () => setUser(null);
const value = { user, login, logout };
return (
// 🟡 Provider가 하위 컴포넌트에게 user 데이터를 공유
<UserContext.Provider value={value}>{children}</UserContext.Provider>
);
};
// 🟡 Context를 사용하는 Custom Hook (사용 간편화)
export const useUser = () => {
const context = useContext(UserContext);
if (!context) {
throw new Error('useUser must be used within a UserProvider');
}
return context;
};- src/App.tsx
// src/App.tsx
import { UserProvider } from './contexts/UserContext';
import UserInfo from './components/UserInfo';
import LoginPanel from './components/LoginPanel';
function App() {
return (
<UserProvider>
{/* 🟡 사용자 정보 제공 */}
<h1>🌐 사용자 관리</h1>
<LoginPanel /> {/* 로그인/로그아웃 버튼 */}
<UserInfo /> {/* 사용자 정보 출력 */}
</UserProvider>
);
}- src/components/UserInfo.tsx
// src/components/UserInfo.tsx
import { useUser } from '../contexts/UserContext';
const UserInfo = () => {
const { user } = useUser(); // 🟠 useContext로 user 값 가져오기
if (!user) return <p>로그인 필요</p>;
return (
<div>
<p>이름: {user.name}</p>
<p>이메일: {user.email}</p>
</div>
);
};- /src/components/LoginPanel.tsx
// src/components/LoginPanel.tsx
import { useUser } from '../contexts/UserContext';
const dummyUser = {
id: 1,
name: '홍길동',
email: 'gildong@example.com',
};
const LoginPanel = () => {
const { user, login, logout } = useUser();
return (
<div>
{user ? (
<>
<p>환영합니다, {user.name}님!</p>
<button onClick={logout}>로그아웃</button>
</>
) : (
<>
<p>로그인이 필요합니다.</p>
<button onClick={() => login(dummyUser)}>로그인</button>
</>
)}
</div>
);
};Context API 업데이트 시점
Context의 값이 변경되었을 때, Provider로 감싸진 모든 자식 컴포넌트가 리렌더링되는 것이 아니라, useContext 또는 Context.Consumer로 해당 Context를 구독하고 있는 컴포넌트만 리렌더링된다.
React는 Context의 value가 변경될 때 다음을 수행한다.
- Provider로 감싸진 하위 트리 전체를 top-down으로 탐색하면서
useContext(SomeContext)혹은<SomeContext.Consumer>를 통해 해당 context를 구독 중인 컴포넌트를 찾아내고- 그 컴포넌트만 리렌더링합니다.
구독하지 않은 컴포넌트는 리렌더링되지 않는다.
아래 예제를 보면,
const MyContext = React.createContext();
function Parent() {
const [value, setValue] = useState(0);
return (
<MyContext.Provider value={value}>
<ChildA /> // useContext로 구독 X
<ChildB /> // useContext로 구독 O
<button onClick={() => setValue((v) => v + 1)}>Increment</button>
</MyContext.Provider>
);
}
function ChildA() {
console.log('ChildA rendered');
return <div>I'm A</div>;
}
function ChildB() {
const val = useContext(MyContext);
console.log('ChildB rendered');
return <div>Value: {val}</div>;
}ChildA는 context를 구독하지 않으므로 리렌더링되지 않는다.
ChildB는 useContext(MyContext)로 context를 구독하므로 context가 바뀔 때마다 리렌더링된다.
주의: 최적화를 하지 않으면 여전히 리렌더링될 수 있는 경우
ChildA가 ChildB를 포함하거나, 상위 컴포넌트에서 리렌더링이 발생하면 그 영향으로 같이 리렌더링될 수 있다.
이런 경우는 React.memo또는 useMemo 등을 통해 최적화해야 한다.
Context API 사용 시 주의사항
useContext()는 단순히 값만 읽는 Hook처럼 보이지만, 값이 바뀌면 컴포넌트가 리렌더링된다.- Provider가 전달하는 객체는 매번 새로 생성되면 안 된다.
const value = useMemo(() => ({ user, login, logout }), [user]);
<UserContext.Provider value={value}>{children}</UserContext.Provider>;요약
| 요소 | 역할 | 특징 |
|---|---|---|
createContext() | Context 생성 | Provider/Consumer 포함 |
<Provider> | 값 전달 | 가장 가까운 Provider의 값이 적용됨 |
useContext() | 값 소비 | Context 값 구독 및 자동 업데이트 |